Introduction
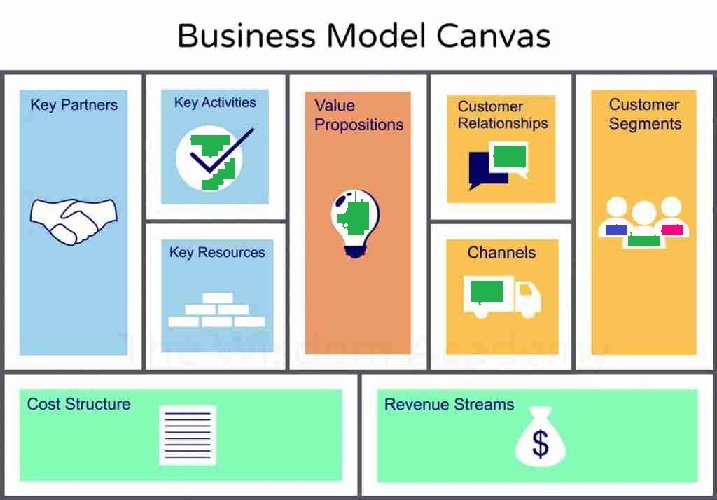
The Business Model Canvas Examples is a strategic tool designed to visualize and streamline your business idea or model. Created by Alexander Osterwalder, it is a one-page framework consisting of nine building blocks that encapsulate key elements of a business. The tool has gained immense popularity among startups, entrepreneurs, and even established corporations for its simplicity and effectiveness.
In this blog, we will:
- Explore detailed business model canvas examples across multiple industries.
- Break down the core components of the BMC framework.
- Provide actionable insights to help you create or refine your own business model.
Let’s dive into the details!
What is a Business Model Canvas?
The Business Model Canvas consists of the following nine sections:
- Customer Segments: The target groups or audiences your business serves.
- Value Propositions: The unique value your product or service offers to customers.
- Channels: The mediums through which you deliver your value proposition.
- Customer Relationships: How you engage with and retain customers.
- Revenue Streams: The income sources from your value propositions.
- Key Resources: Assets needed to deliver your value proposition.
- Key Activities: The crucial tasks your business must perform.
- Key Partnerships: Collaborations to leverage your business operations.
- Cost Structure: The expenses incurred in running your business model.
Each block is interconnected, making it essential to view the canvas as a whole system rather than isolated parts.
Why Use the Business Model Canvas?
Using the Business Model Canvas has several benefits:
- Clarity: It simplifies complex business ideas into a single-page visualization.
- Strategic Alignment: Helps align team members with the business goals.
- Flexibility: Easily adaptable for brainstorming and testing new ideas.
- Focus on Value: Keeps your attention on delivering value to customers.
Examples of Business Model Canvases
1. Airbnb
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Customer Segments | Travelers looking for affordable stays, hosts seeking additional income. |
| Value Propositions | Affordable, unique stays; supplemental income for hosts. |
| Channels | Website, mobile app, social media. |
| Customer Relationships | Peer reviews, customer support, loyalty programs. |
| Revenue Streams | Commission on bookings, service fees from guests. |
| Key Resources | Technology platform, user database, brand reputation. |
| Key Activities | Platform maintenance, marketing, customer support. |
| Key Partnerships | Payment gateways, property management services. |
| Cost Structure | Technology development, customer acquisition, operational support. |
Analysis:
Airbnb disrupted the hospitality industry by offering an alternative to traditional hotel accommodations. Its model emphasizes a platform economy, connecting two groups (hosts and travelers) while maintaining low operational costs.
2. Tesla
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Customer Segments | Environmentally conscious consumers, tech enthusiasts, premium buyers. |
| Value Propositions | High-performance electric vehicles, innovative energy solutions. |
| Channels | Company-owned showrooms, online sales, service centers. |
| Customer Relationships | Direct sales model, personalized customer care. |
| Revenue Streams | Vehicle sales, energy products, software subscriptions. |
| Keys Resources | R&D, patents, manufacturing facilities, skilled workforce. |
| Key Activities | Innovation, manufacturing, marketing, sales. |
| Key Partnerships | Battery suppliers, autonomous technology developers. |
| Cost Structure | Manufacturing, R&D, marketing, distribution. |
Analysis:
Tesla’s business model focuses on vertical integration and innovation, ensuring control over critical aspects like battery production and autonomous driving technology.
Key Insights for Crafting Your Business Model Canvas
- Prioritize the Value Proposition
Your value proposition should address a critical problem or create a significant opportunity for your target customers. Use clear, compelling language that resonates with your audience.
- Understand Your Customer Segments
Segment your audience by demographics, preferences, and behaviors. For instance, a fitness app might target both fitness enthusiasts and beginners but offer tailored experiences for each group.
- Utilize Data to Define Revenue Streams
Analyze your industry and customer base to diversify your revenue streams. E-commerce platforms, for example, might earn from direct sales, advertisements, and subscription models.
- Collaborate Effectively
Form partnerships that enhance efficiency or expand market reach. For instance, ride-hailing apps often collaborate with local vehicle leasing companies to onboard drivers.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case Study 1: Uber
Uber operates on a multi-sided platform model, connecting drivers and riders.
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Customer Segments | Riders (affordable transport), drivers (income opportunities). |
| Value Propositions | Convenience, affordability, flexibility for drivers. |
| Channels | Mobile app, online marketing, partnerships. |
| Customer Relationships | Self-service app, customer support. |
| Revenue Streams | Ride fares, service fees. |
| Key Resources | App infrastructure, driver network, brand trust. |
| Key Activities | Platform development, driver acquisition, customer service. |
| Key Partnerships | Payment processors, map services, vehicle manufacturers. |
| Cost Structure | Marketing, app development, operational expenses. |
Case Study 2: IKEA
IKEA’s business model is centered around affordable, self-assembly furniture.
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Customer Segments | Budget-conscious families, young adults, small businesses. |
| Value Propositions | Affordable, stylish furniture; eco-friendly materials. |
| Channels | Retail stores, e-commerce, catalogs. |
| Customer Relationships | Self-service stores, online tools, after-sales service. |
| Revenue Streams | Product sales, additional services (delivery, assembly). |
| Key Resources | Supply chain, retail locations, design team. |
| Key Activities | Product design, supply chain management, retail operations. |
| Key Partnerships | Suppliers, logistics providers, recycling organizations. |
| Cost Structure | Manufacturing, logistics, marketing, retail. |
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Ignoring Customer Feedback: Your value proposition must evolve based on customer needs.
- Overlooking Costs: Failing to calculate expenses accurately can disrupt operations.
- Poor Partnerships: Align with partners that enhance, not hinder, your objectives.
Conclusion
The Business Model Canvas Examples is a versatile tool for startups, SMEs, and large corporations alike. By studying these examples and tailoring the framework to your business, you can gain clarity, streamline operations, and innovate effectively.